San and Ovahakaona Tribes
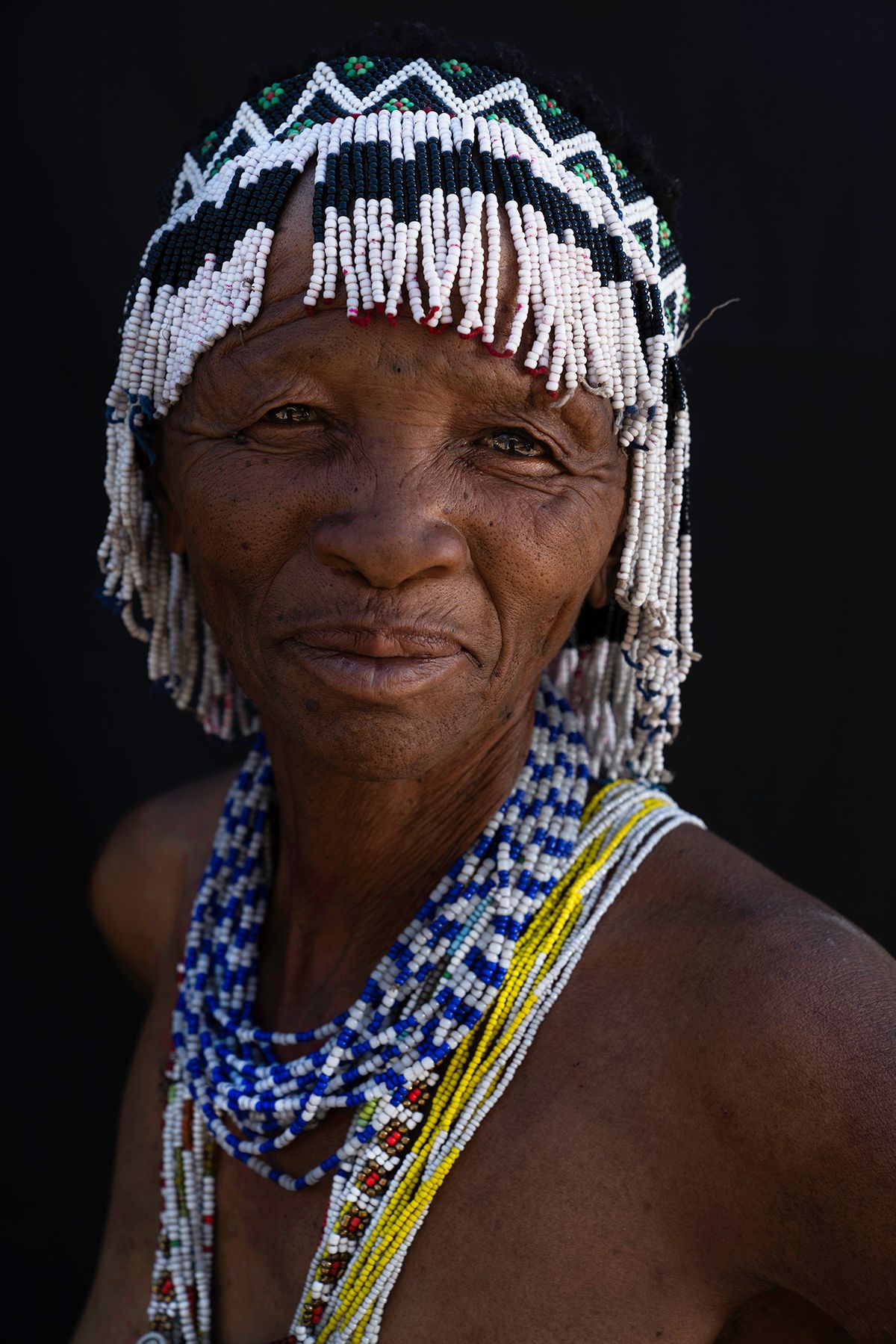
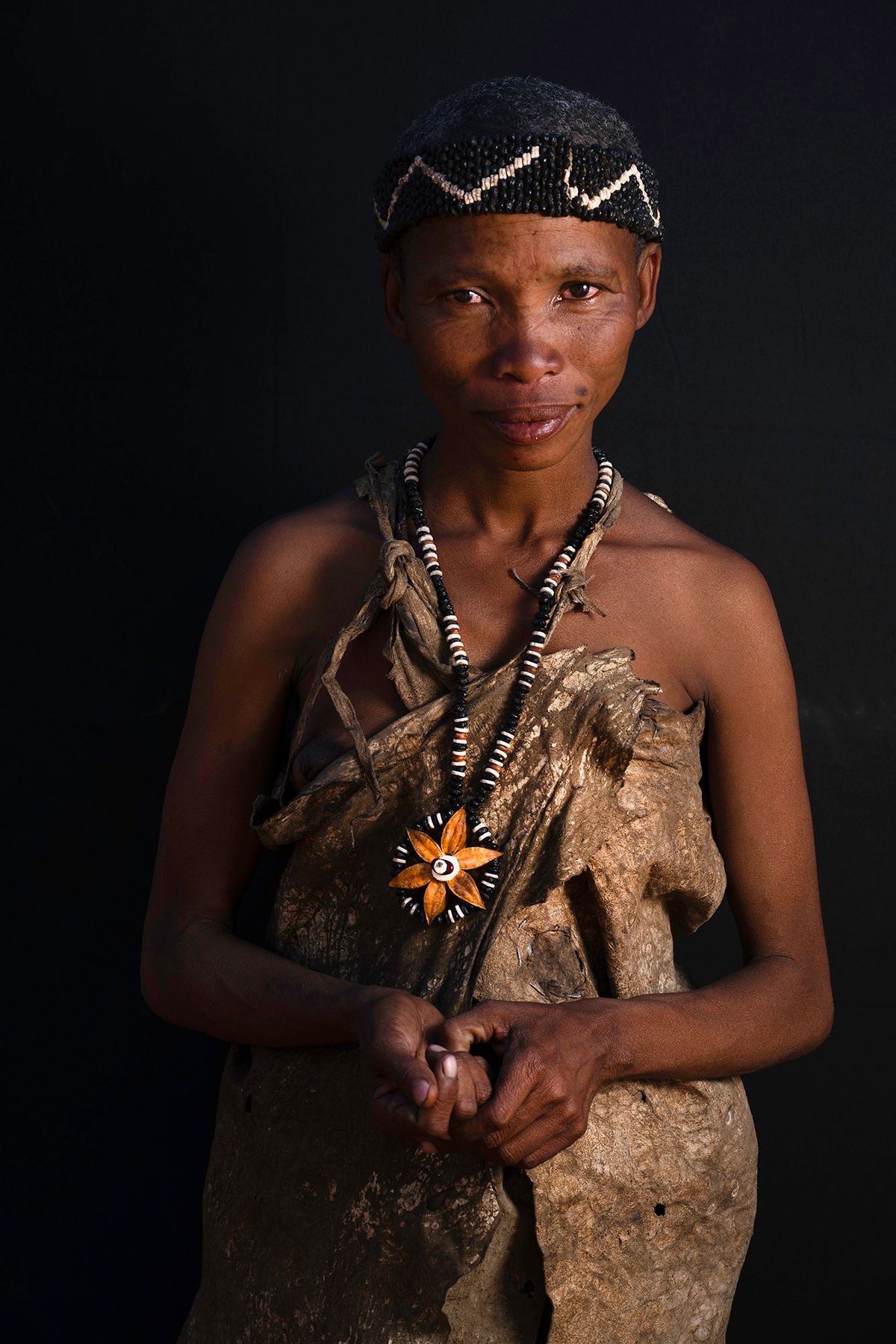
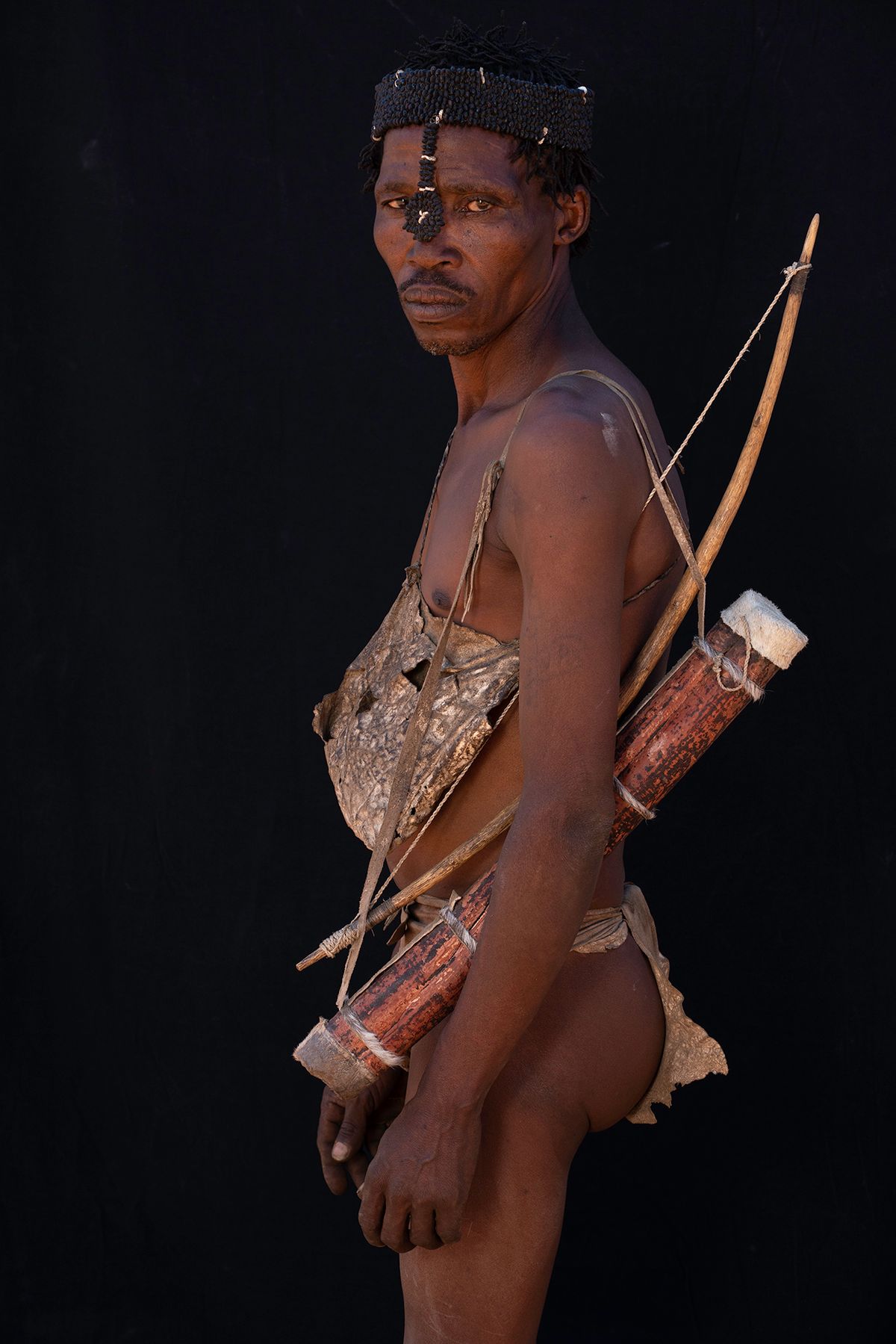
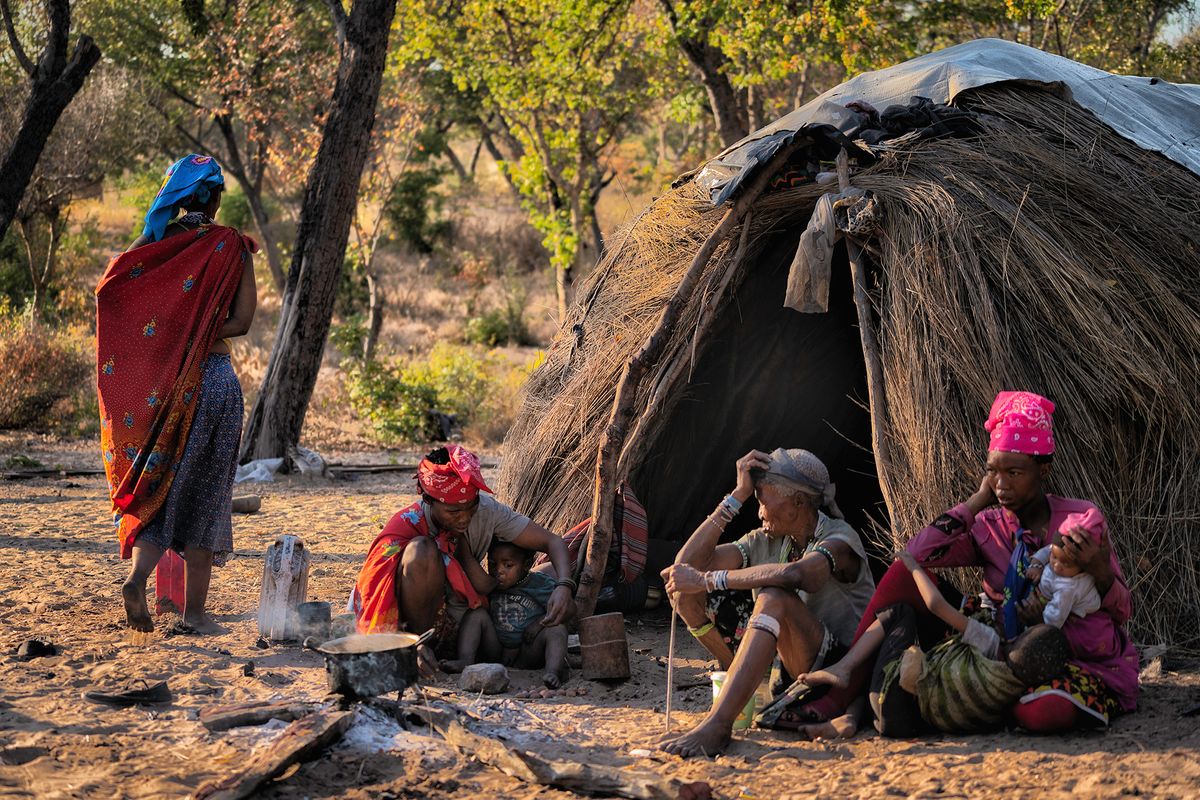
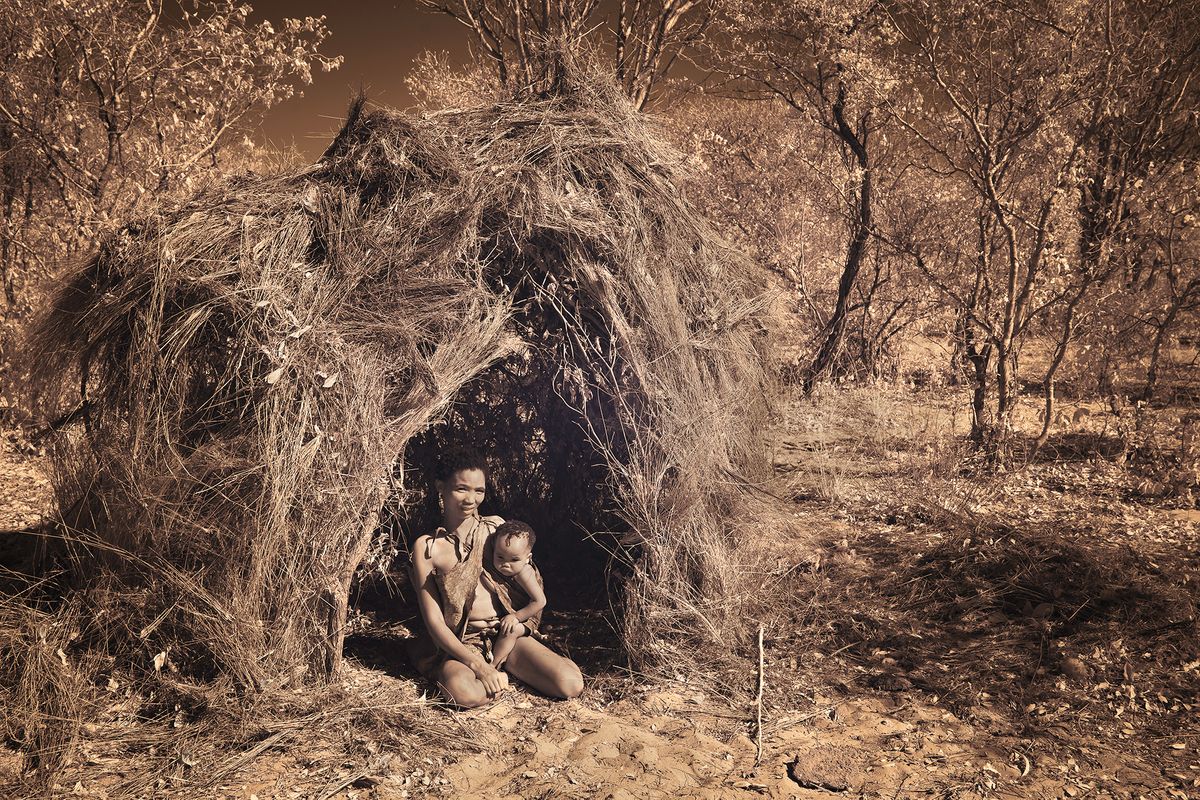
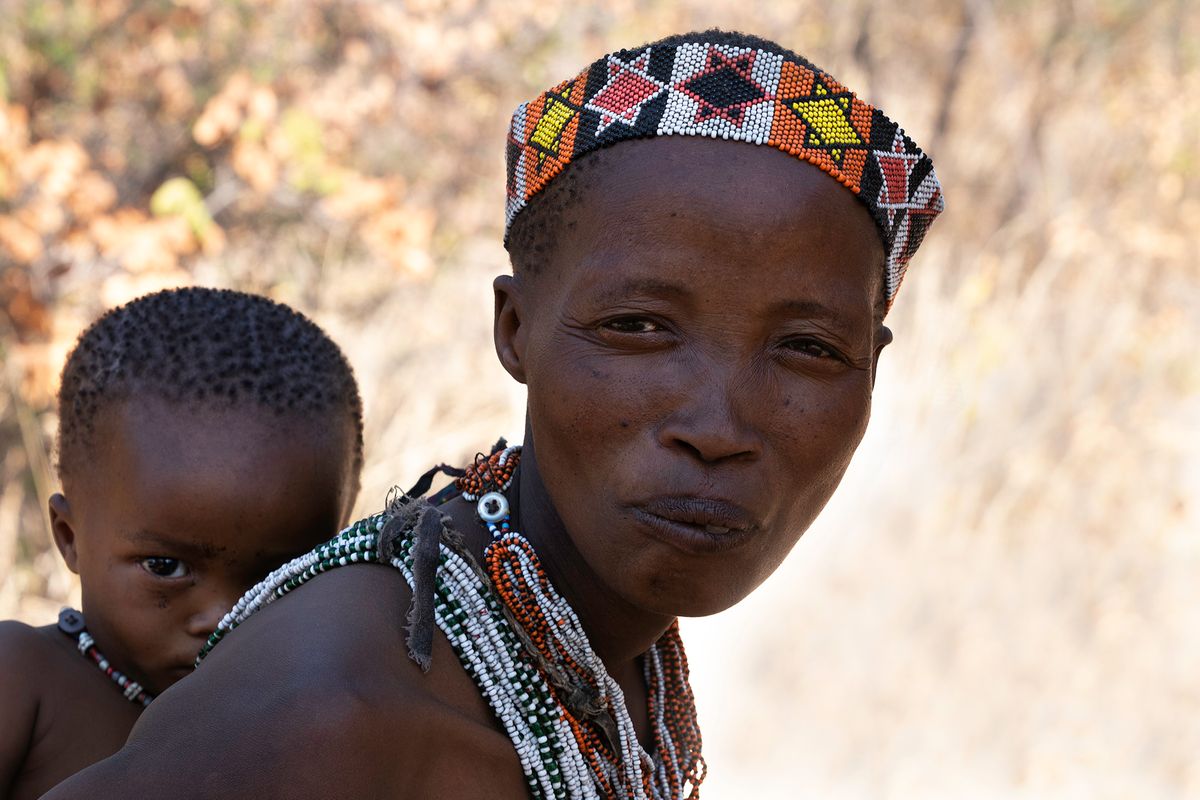
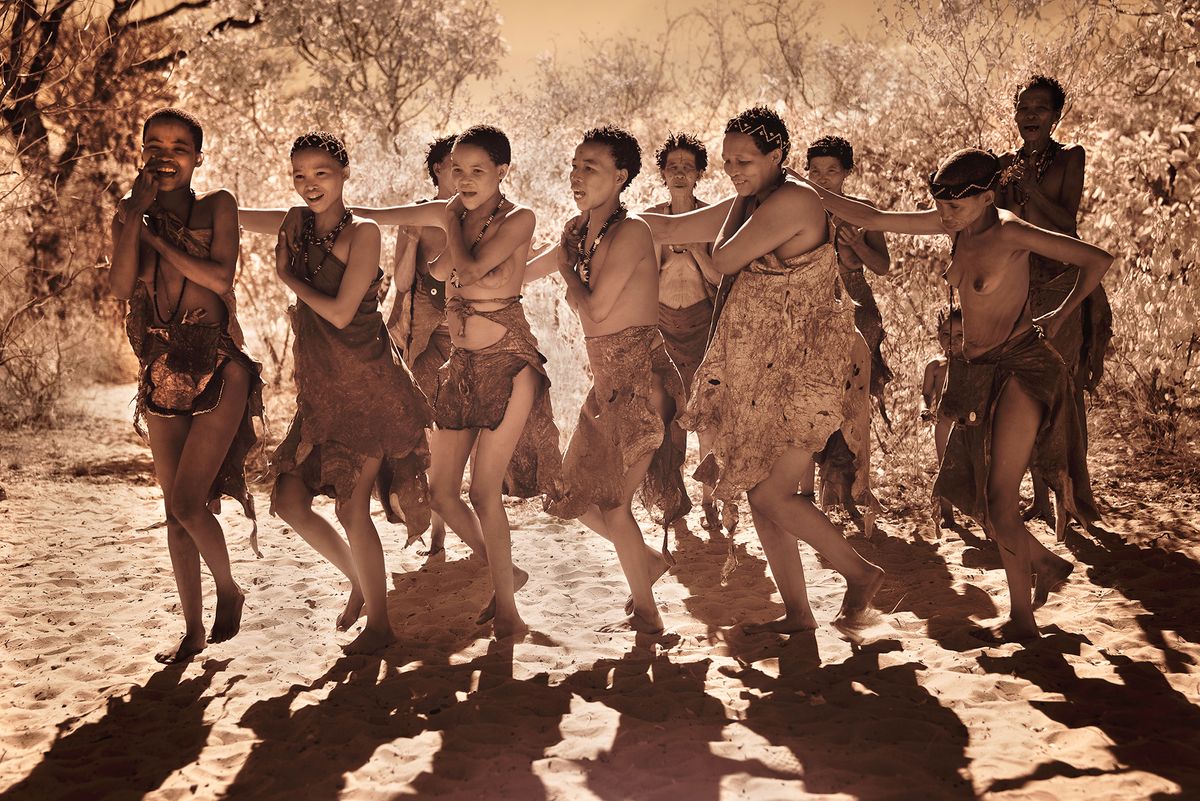
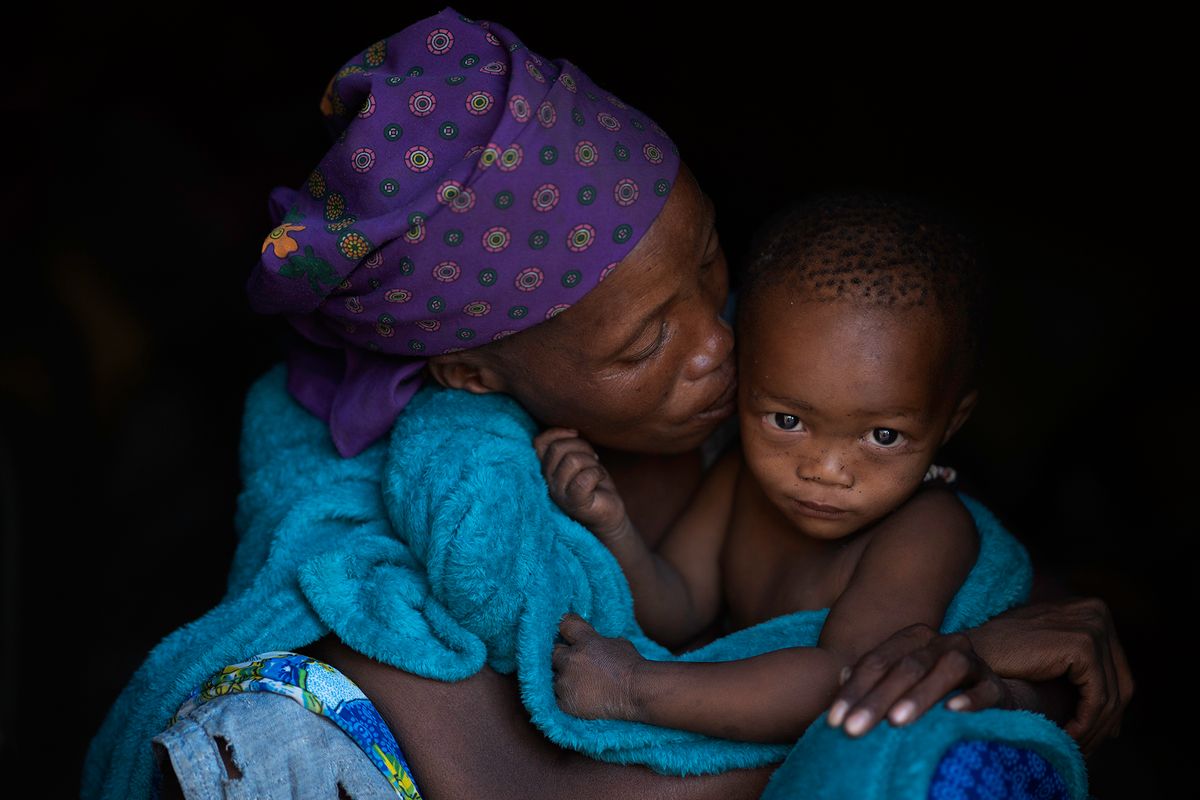
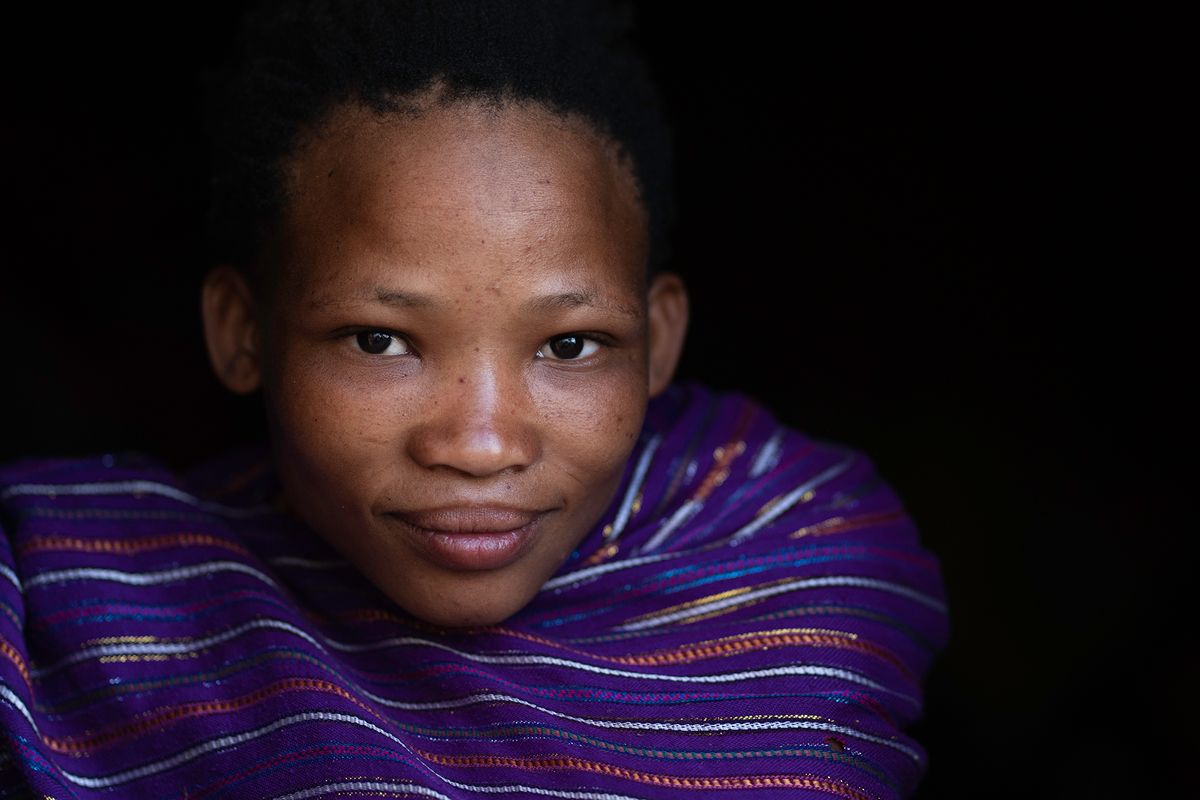
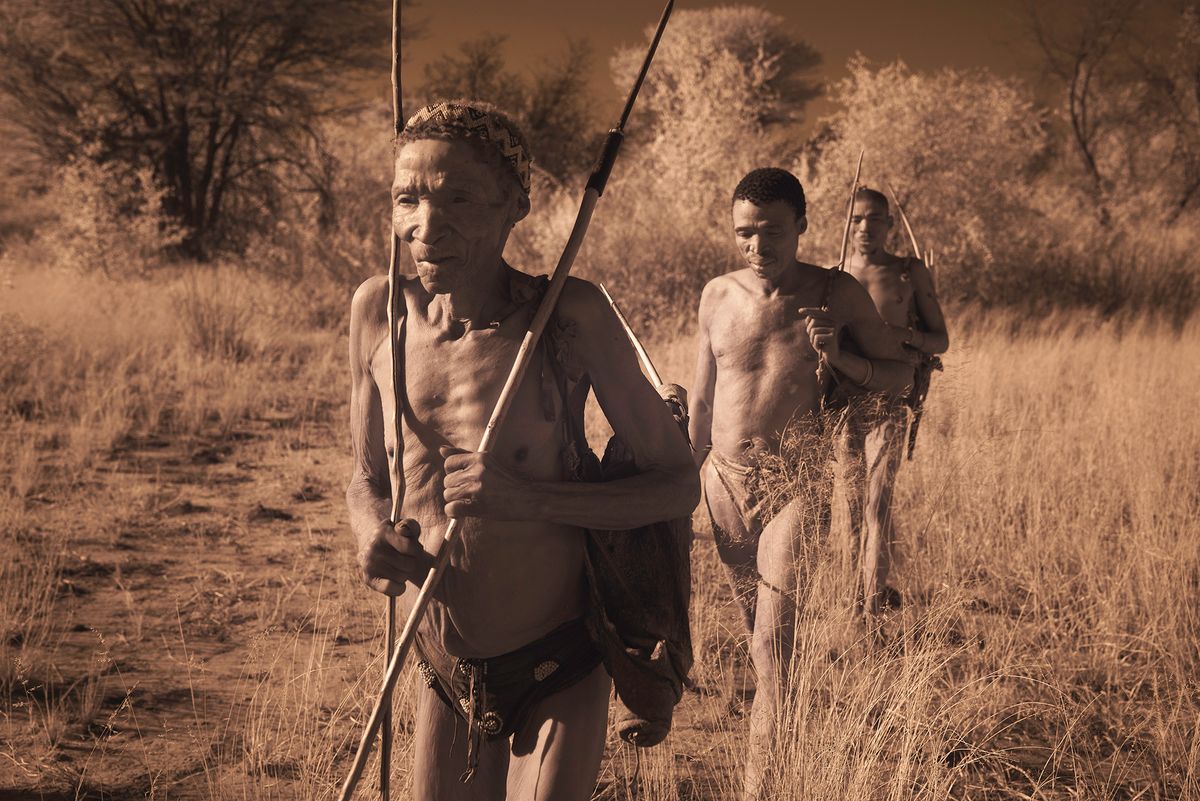
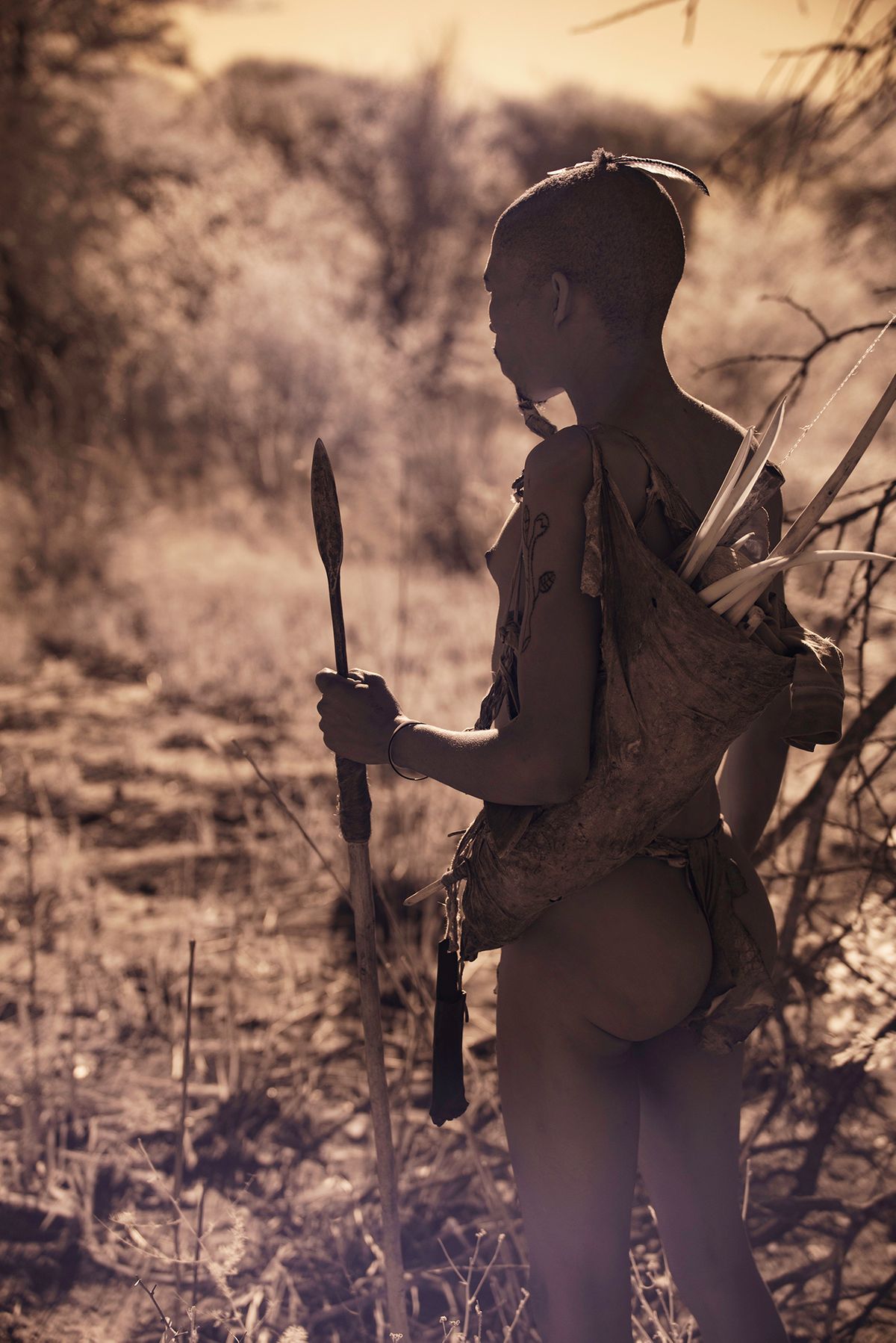
"San" is a collective name for Khoisan-speaking nations in Southern Africa. Also sometimes referred to as Bushmen. Or Ju'Hoansi San.
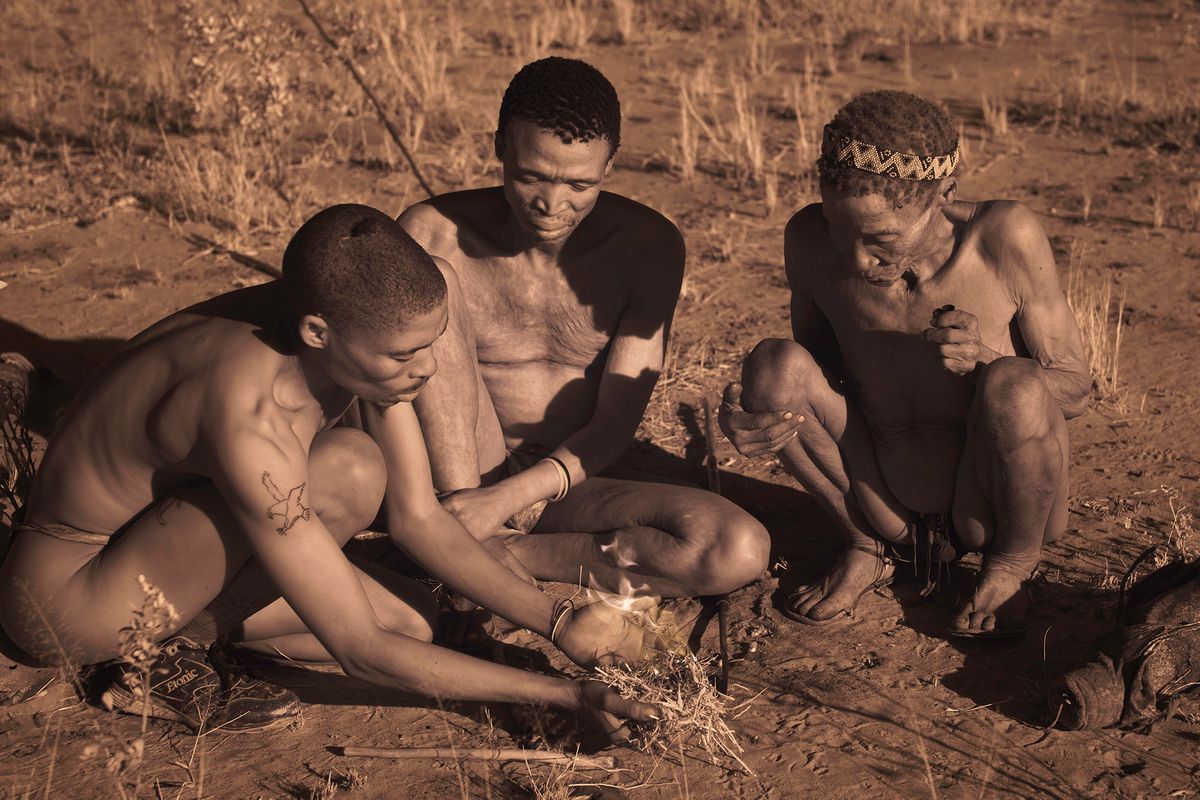
The San are the descendants of the first Homo sapiens, i.e. modern man. They have the oldest gene pattern of any existing people and it is thought that all other nationalities are descended from them. Historically, the San were hunter-gatherers who maintained a semi-nomadic lifestyle. This meant that they moved throughout the year in accordance with the availability of water, game and the edible plants that they used to substitute their diet.
The San are an egalitarian people and traditionally have no official leader or chief. Women are considered equal, and decisions are made as a group. When disagreements arise, lengthy discussions are held to resolve any issues.
Today, it is estimated that there are around 100,000 San still living in Southern Africa. They are divided into 35 linguistic groups and only a very small fraction are able to live according to their traditional lifestyle.
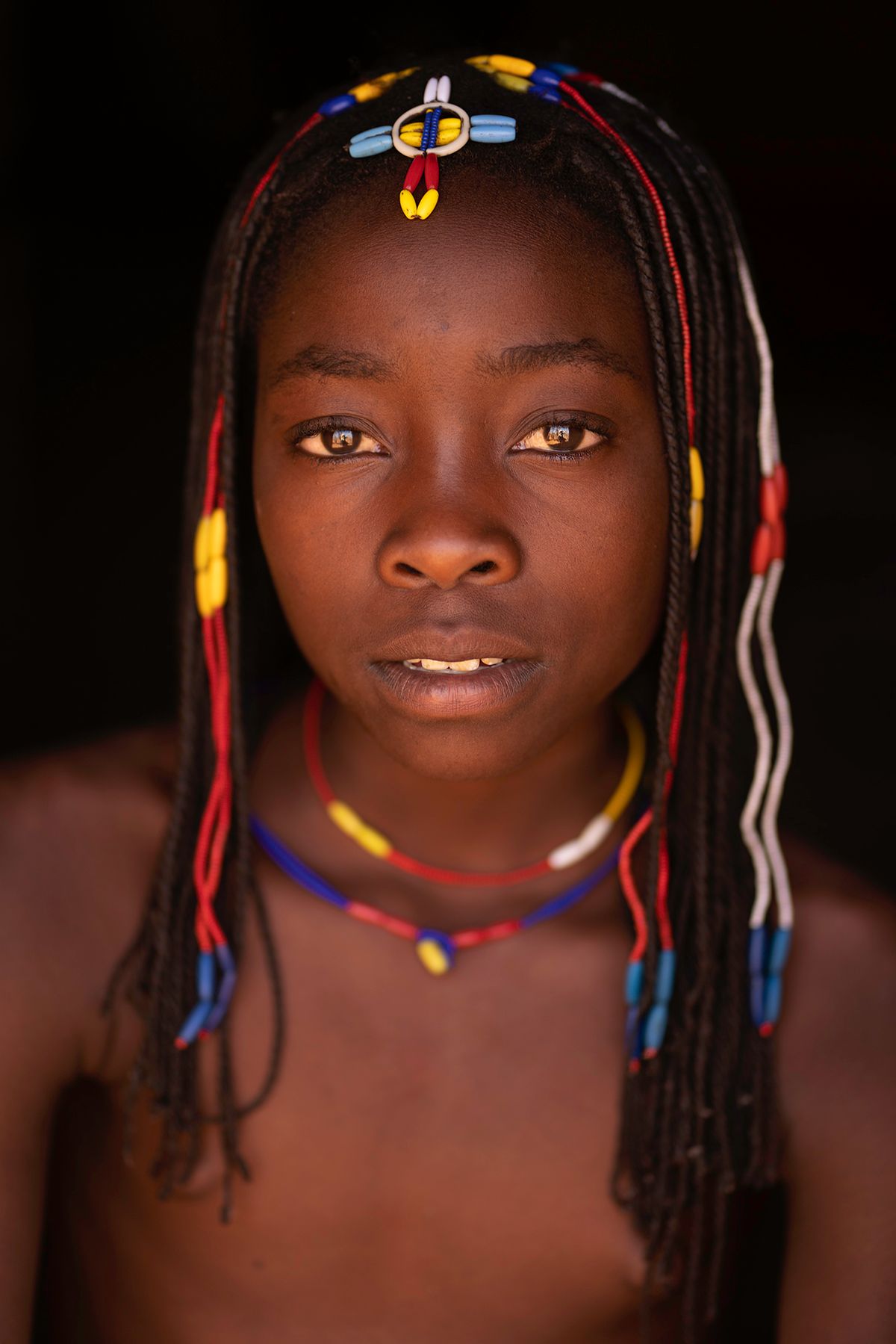
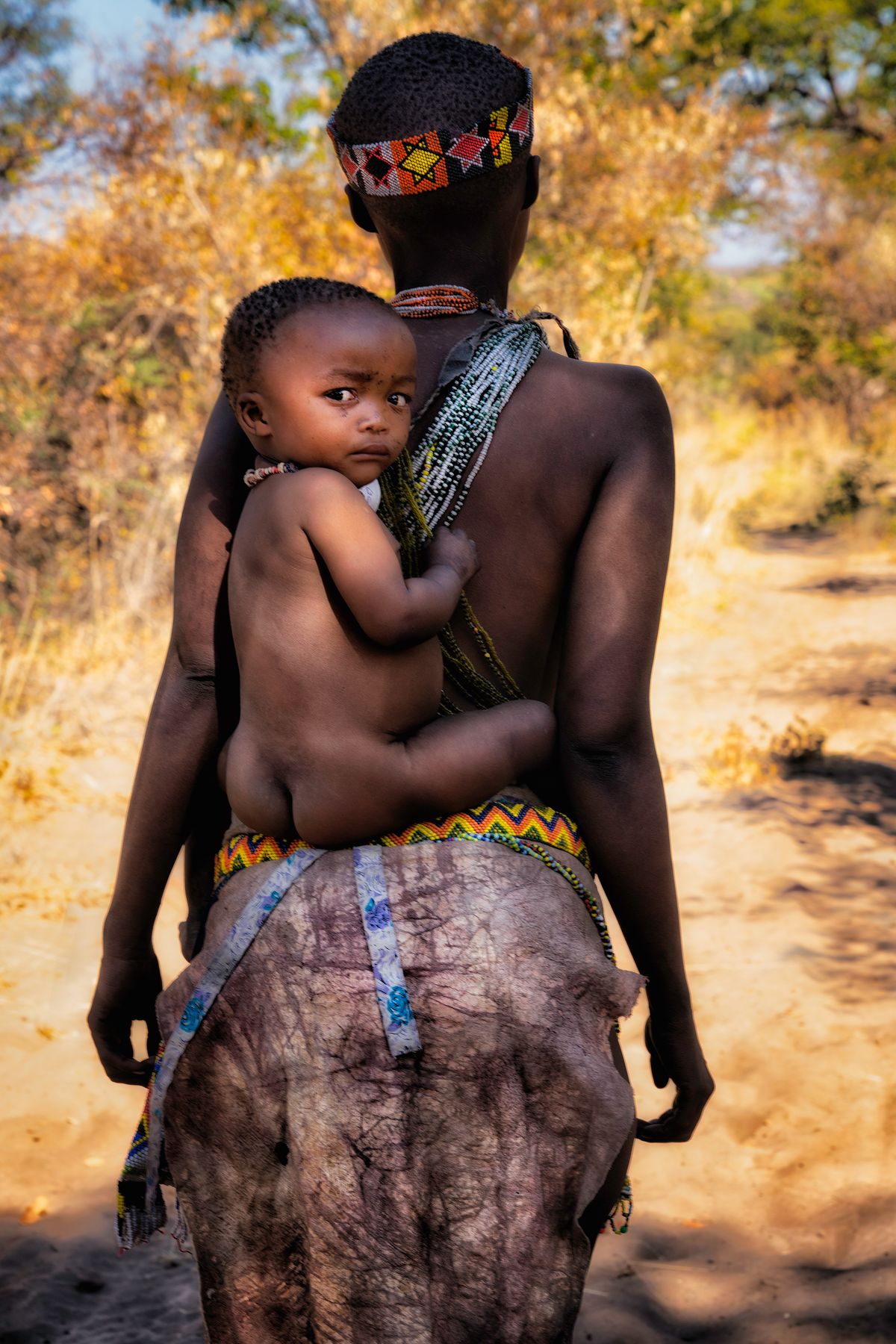
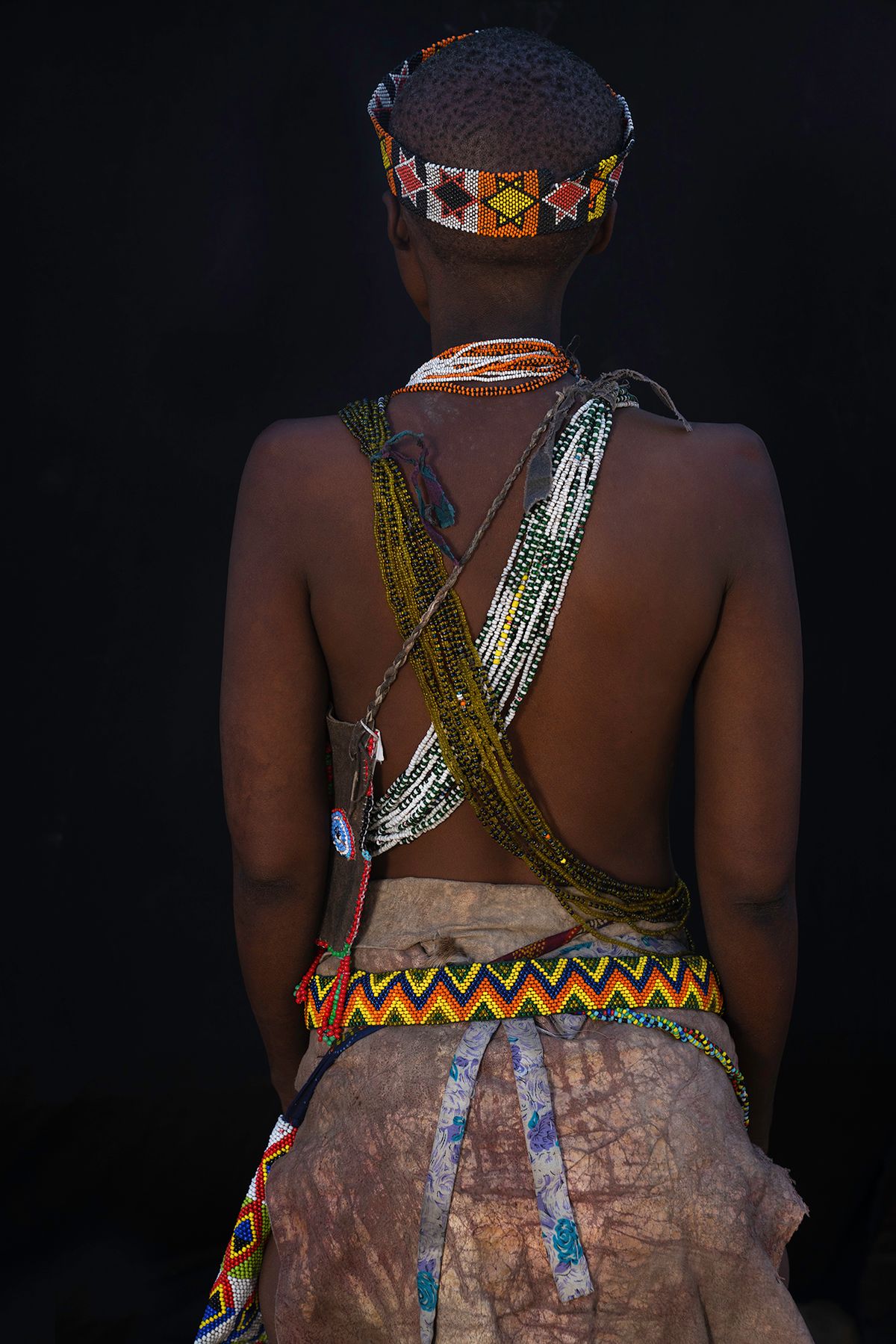
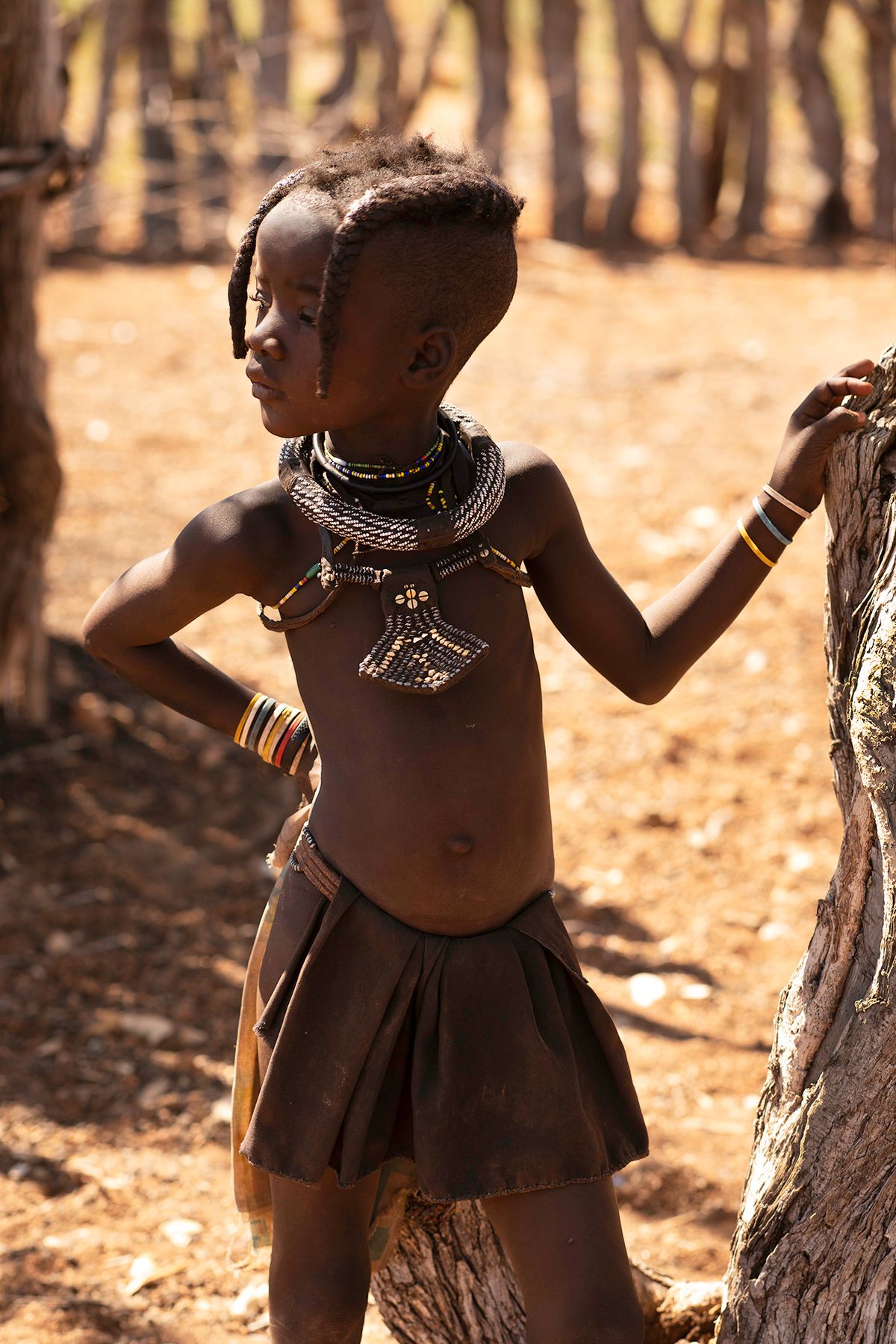
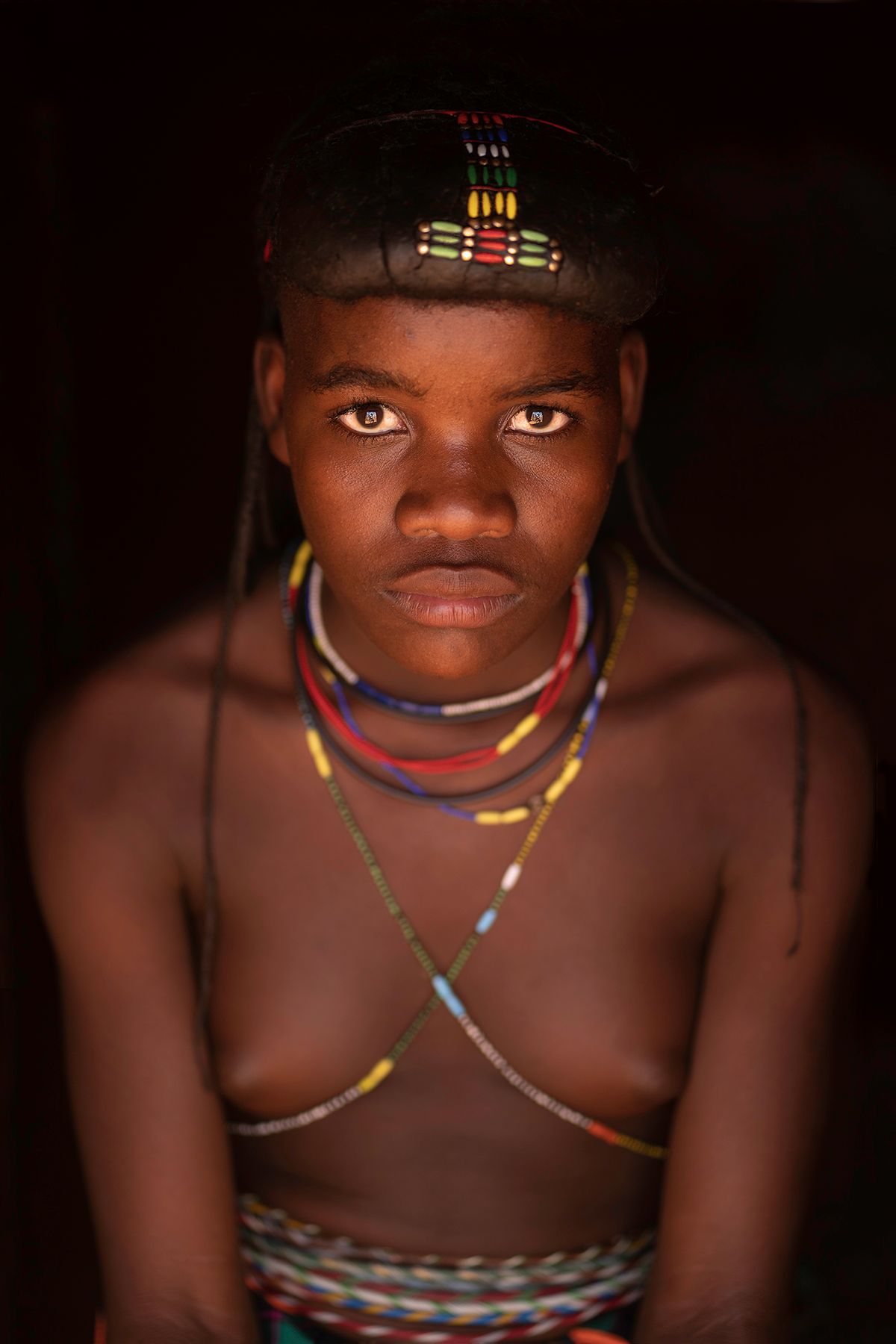
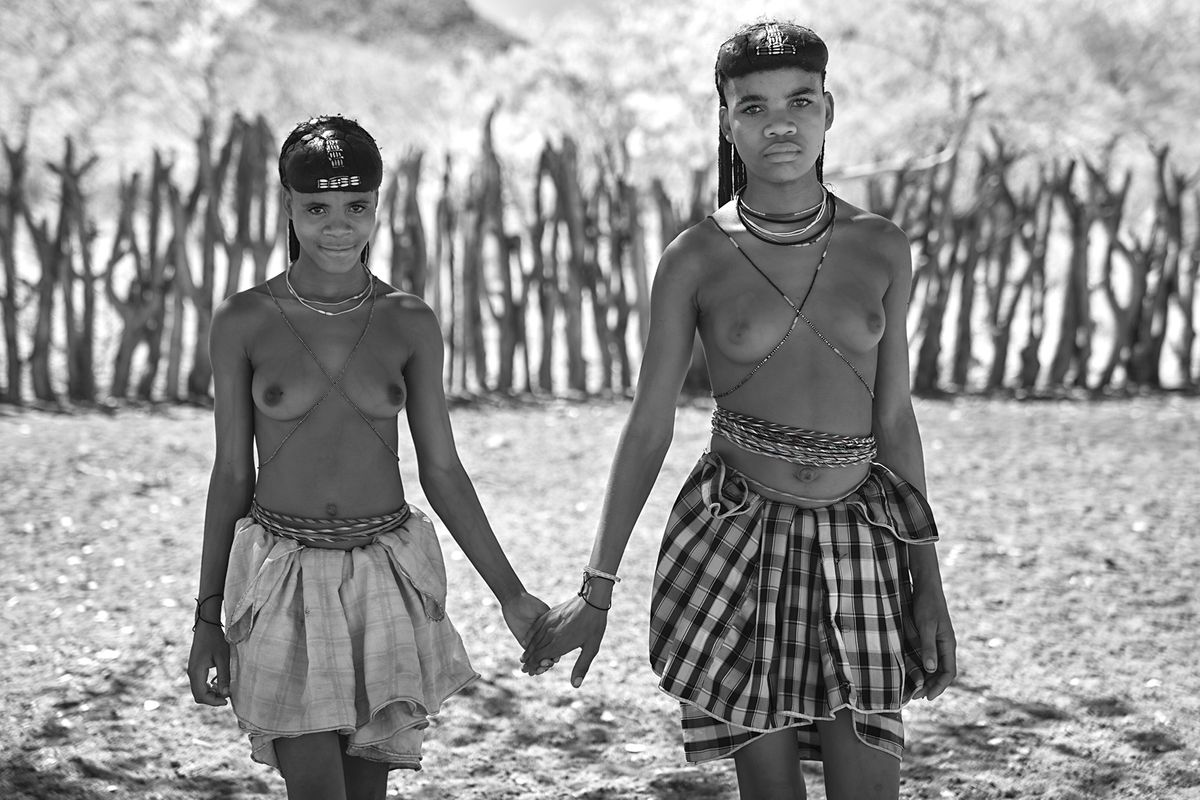
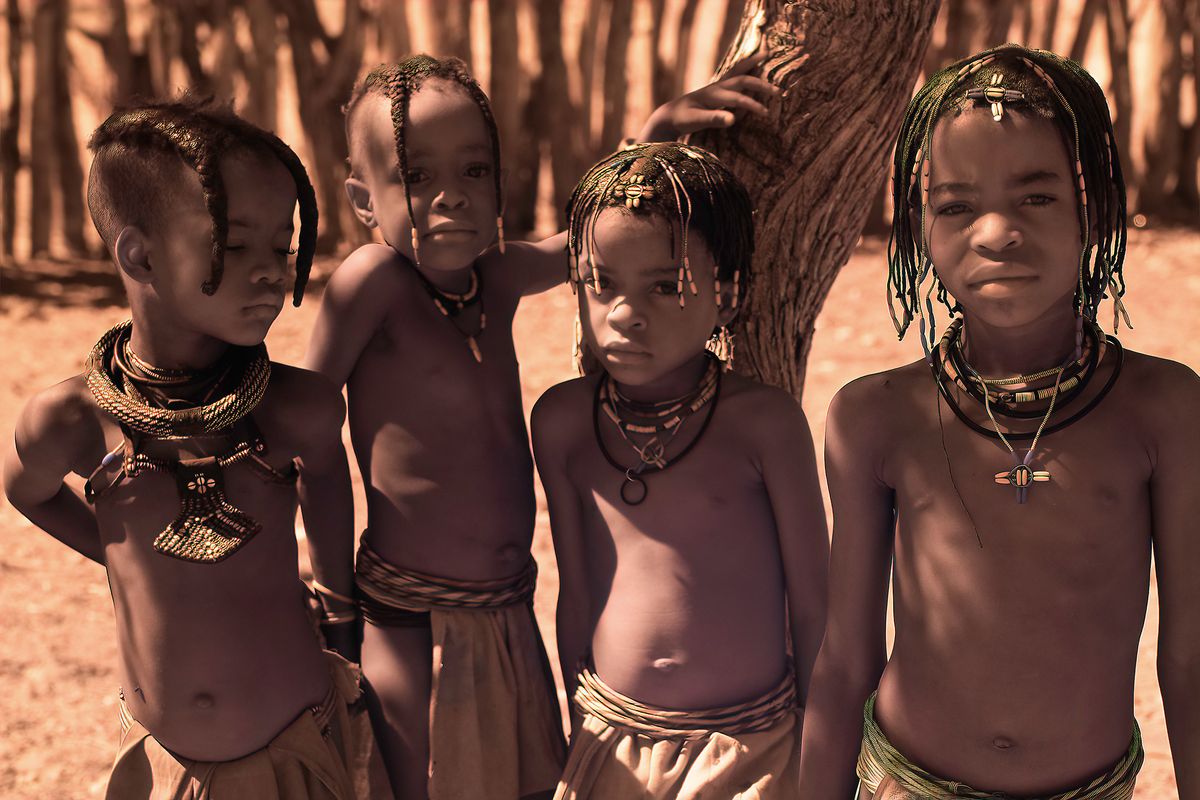
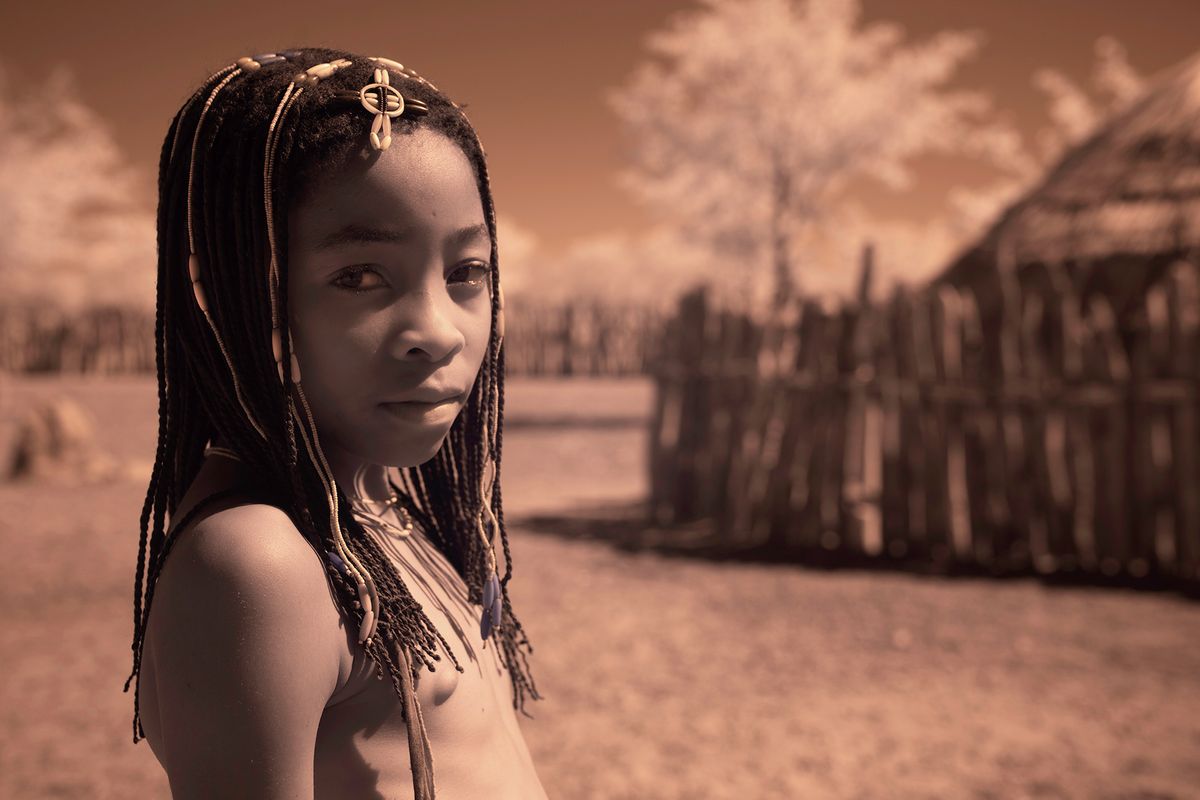
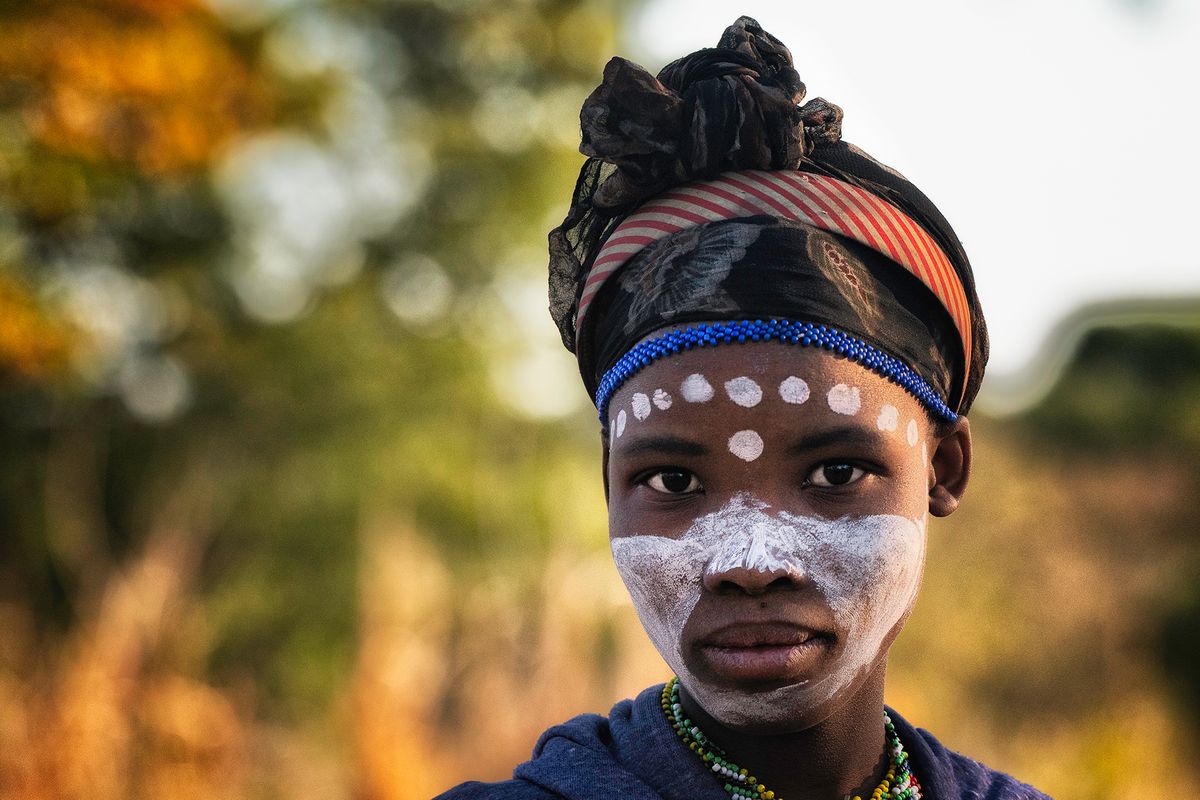
The Ovahakaona are a part of the Ova Himba Tribal Tradition.
The Ovahakaona ladies adorn their bodies with colorful body chains across their chests and around their waists. An ensemble of colorful and attractive fabrics make a beautiful skirt for both the Ovahakaona and Ovahimba women.